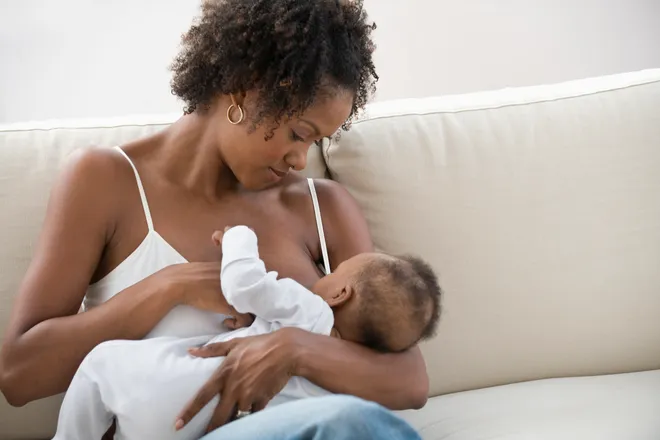
It is generally recommended that breastfeeding mothers avoid drinking alcohol, or at least limit their alcohol intake. This is because alcohol can pass into breast milk and affect the baby.
The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests that breastfeeding mothers wait at least 2 hours after a single serving of alcohol before nursing their baby. If you plan to have more than one drink, it’s recommended to wait longer before nursing to ensure that the alcohol has cleared your system.
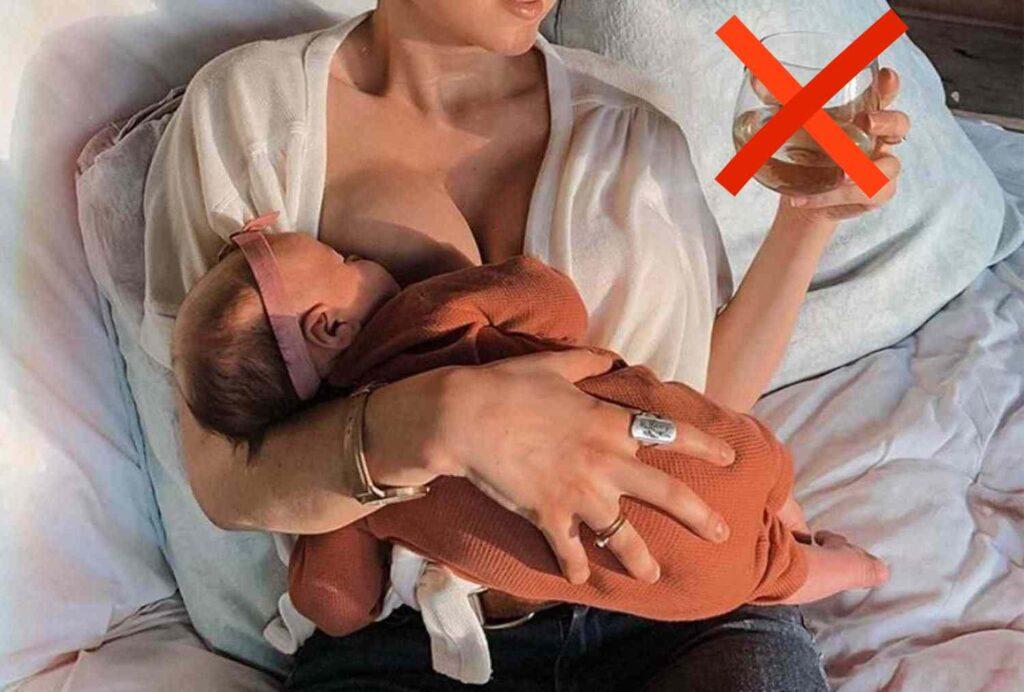

It’s also important to know that the amount of alcohol that is passed through breast milk is equivalent to the amount of alcohol in your bloodstream. Factors that can affect this include your weight, how quickly you metabolize alcohol, and the type and amount of alcohol you consume.
If you do choose to drink while breastfeeding, it’s important to plan ahead and make sure that you have a safe and reliable way to care for your baby while you’re under the influence. Alternatively, you could consider pumping and storing breast milk before drinking, and feeding your baby with that milk while the alcohol is still in your system.
WHEN TO STOP BREASTFEEDING
The decision to stop breastfeeding is a personal one that can depend on a variety of factors, including the mother’s physical and emotional health, the baby’s needs and development, and lifestyle factors such as work and childcare.
In terms of the baby’s needs, the World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding alongside complementary foods for up to two years or beyond.
Some mothers may choose to stop breastfeeding earlier than this for various reasons, such as a return to work or a desire to wean the baby. It’s important to make the decision to stop breastfeeding based on what feels right for you and your baby, and to do so in a gradual and supportive way that minimizes any discomfort or distress for either of you.
If you’re considering stopping breastfeeding, it can be helpful to talk to your healthcare provider or a lactation consultant for guidance and support. They can help you develop a plan for weaning your baby that takes into account your individual circumstances and needs.
HOW TO STOP BREASTFEEDING
If you’re considering stopping breastfeeding, it’s important to do so gradually and with sensitivity to your baby’s needs.
Here are some tips for stopping breastfeeding:
- Start slowly: Begin by reducing the number of breastfeeding sessions gradually, over a period of several weeks. This can help to minimize discomfort and reduce the risk of engorgement or blocked milk ducts.
- Offer a bottle or cup: As you reduce breastfeeding sessions, you can introduce a bottle or cup of expressed breast milk or formula. This can help to satisfy your baby’s hunger and reduce their reliance on breastfeeding.
- Substitute with solid foods: As your baby grows, you can gradually introduce solid foods to their diet to replace breast milk. This can help to satisfy their nutritional needs and reduce their need for breast milk.
- Comfort your baby: As you reduce breastfeeding sessions, your baby may become fussy or irritable. It’s important to offer comfort and reassurance through cuddling, rocking, or other forms of physical contact.
- Take care of yourself: Stopping breastfeeding can be an emotional experience for both you and your baby. It’s important to take care of yourself by eating well, staying hydrated, and getting plenty of rest.
CAN YOU GET PREGNANT WHILE BREASTFEEDING?
Yes, it is possible to get pregnant while breastfeeding. While breastfeeding can suppress ovulation in some women, it is not a reliable method of contraception and should not be relied upon as the sole means of preventing pregnancy.
The chances of becoming pregnant while breastfeeding depend on a variety of factors, including how often and how long you breastfeed, the age of your baby, and whether or not your menstrual cycle has returned.
Breastfeeding can suppress ovulation by reducing the production of the hormones that trigger ovulation. However, this effect is not reliable and can vary from woman to woman. Additionally, ovulation can occur before you have your first postpartum period, which can make it difficult to predict when you are most fertile.
If you’re breastfeeding and want to prevent pregnancy, it’s important to use a reliable form of contraception, such as condoms or a hormonal method of birth control. You can talk to your healthcare provider about the best options for you.
HOW TO LOSE WEIGHT WHILE BREASTFEEDING
Losing weight while breastfeeding can be challenging because your body needs extra nutrients and calories to produce breast milk. However, it is possible to lose weight in a safe and healthy way while still ensuring that your baby is getting the nutrients they need.
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet: Focus on eating nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid crash diets or extreme calorie restriction, which can reduce milk production and may be harmful to both you and your baby.
- Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated is important for milk production and can also help you feel full and satisfied.
- Get regular exercise: Incorporate moderate exercise into your routine, such as brisk walking, yoga, or swimming.
- Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks: These foods can be high in calories and low in nutrients, and can contribute to weight gain.
- Breastfeed frequently: Breastfeeding can help you burn extra calories and can also help regulate your appetite.
- Get enough sleep: Getting adequate sleep is important for maintaining a healthy weight and can also help reduce stress and fatigue.
In Summery:
Breastfeeding can provide many benefits for both you and your baby, including improved nutrition, immune support, and bonding, its important to Seek support, It can be helpful to seek support from a healthcare provider, lactation consultant, or breastfeeding support group. These resources can provide guidance, information, and emotional support as you navigate the breastfeeding journey.

![DJ R2 - Naija Old school [Throwback Mixtape]](https://speedup9ja.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/dj-r2-mix-150x150.jpg)